are you ready for the ultimate showdown between two notorious pox diseases? In one corner, we have the long-established champion – Chickenpox. And in the other corner, an up-and-coming contender making waves in recent years – Monkeypox vs Chickenpox. Get ready to witness a battle like no other as we delve into their similarities, differences, and everything you need to know about these formidable foes. Brace yourself for “The Battle of the Pox: Monkeypox vs Chickenpox – A Comprehensive Comparison.”
Introduction: The Impact of Pox on Human Health
Pox is a highly contagious viral infection that has plagued human health for centuries. It is caused by the variola virus, which belongs to the family Poxviridae. The word “pox” comes from the Latin word “pustule,” meaning a blister or pimple. This name accurately describes the characteristic skin lesions that are a hallmark of this disease.
The history of pox dates back to ancient times, with evidence of smallpox outbreaks found in Egyptian mummies dating back to 1570 BC. It was also known as the “speckled monster” and had a mortality rate of up to 30%, making it one of the deadliest diseases in human history.
Smallpox was declared eradicated by the World Healthhttps://health.osu.edu/health/virus-and-infection/think-your-rash-might-be-monkeypox-or-chickenpox Organization (WHO) in 1980 after a successful global vaccination campaign. However, another type of pox virus, known as monkeypox, continues to pose a threat to human health in certain parts of Africa and Asia.
In this blog post, we will explore the impact of pox on human health and compare two closely related viruses – monkeypox and chickenpox – that have been causing confusion among people due to their similar names and symptoms.
The Impact Of Pox On Human Health:
Pox infections can cause mild illness or severe disease depending on the type of virus involved and an individual’s immune system response. The most common types of pox infections include smallpox, cowpox ,Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
What is Monkeypox? Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
Monkeypox vs Chickenpox is a rare viral disease that is caused by the monkeypox virus, which belongs to the family Poxviridae. The virus was first identified in 1958 when it was discovered in captive monkeys in Denmark, hence the name “monkeypox.” Although the virus primarily affects primates, including monkeys and African rodents, it can also infect humans. Cases of monkeypox have been reported mainly in Central and West Africa, with sporadic outbreaks occurring in other parts of the world.
Transmission:
Monkeypox vs Chickenpox is transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or animal products such as blood, body fluids, or skin lesions. It can also be spread through respiratory droplets from an infected person’s cough or sneeze. Another possible mode of transmission is through bites or scratches from infected animals. Additionally, contact with contaminated objects such as bedding or clothes can also lead to infection.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of Monkeypox vs Chickenpox are similar to those of smallpox and Monkeypox vs Chickenpox, making it challenging to diagnose without laboratory tests. The initial symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, and exhaustion – similar to many common illnesses like influenza. This makes it difficult for healthcare professionals to identify monkeypox early on. As the illness progresses over 1-3 weeks after exposure, patients may develop a rash which starts on the face and spreads throughout the body.
The rash typically begins as small red bumps that eventually turn into fluid-filled blisters. These blisters
Definition and History
Definition:
Monkeypox and chickenpox are two viral infections that share some similarities, but also have distinct differences. Both diseases are caused by viruses belonging to the poxvirus family. However, they are caused by different strains of the virus and have different modes of transmission.
History:
The history of Monkeypox vs Chickenpox can be traced back to 1958, when it was first discovered in laboratory monkeys in Copenhagen, Denmark. The virus responsible for monkeypox was named after the laboratory where it was first isolated – the State Serum Institute in Copenhagen.
The first recorded human case of monkeypox occurred in 1970 in a nine-year-old boy from Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo). However, it wasn’t until 1971 that the disease gained international recognition when outbreaks were reported in various African countries including Liberia, Sierra Leone and Ivory Coast.
In contrast, Monkeypox vs Chickenpox has been known since ancient times. In fact, it is believed that Egyptian hieroglyphics dating back to around 1500 BC depict people with characteristic lesions of chickenpox. It wasn’t until the early 20th century that scientists identified the varicella-zoster virus as the cause of Monkeypox vs Chickenpox.
Despite being well-known for centuries, widespread vaccination against Monkeypox vs Chickenpox only began in 1995 with the introduction of a vaccine developed by Merck & Co., Inc.
Geographical distribution:
Monkeypox vs Chickenpox is primarily found in remote areas of Central and West Africa. Out
Causes and Transmission
Causes:
Monkeypox and chickenpox are both caused by viruses, but they belong to different families. Monkeypox is caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), which belongs to the Ortho poxvirus family. Chickenpox, on the other hand, is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which belongs to the Herpesviridae family.
Transmission:
Monkeypox and chickenpox are both highly contagious diseases that can easily spread from person to person through direct contact with infected individuals or their bodily fluids. However, there are some differences in how these viruses are transmitted. Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
- Direct Contact:
Both monkeypox and chickenpox can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected individual’s skin lesions or blisters. In monkeypox, this can also include contact with infected animals such as monkeys, squirrels, rats, and other rodents that may carry the virus. Similarly, in chickenpox, touching an infected person’s skin lesions or blisters can result in transmission of the virus.
- Respiratory Route:
The most common mode of transmission for both monkeypox and chickenpox is through respiratory secretions like saliva or mucus droplets when an infected individual coughs or sneezes. These droplets can then be inhaled by someone nearby and cause infection. Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
- Indirect Contact:
Indirect contact with contaminated objects or surfaces can also lead to transmission of these viruses
Symptoms and Severity
Symptoms and severity are key factors to consider when comparing two diseases, especially when they share similar characteristics like monkeypox and chickenpox. While both diseases can cause rashes and blisters on the skin, there are significant differences in their symptoms and severity.
Symptoms of Monkeypox:
Monkeypox is a rare viral disease that is primarily found in Central and West Africa. It is caused by the Monkeypox virus, which belongs to the same family as smallpox. The symptoms of monkeypox typically manifest within 5-21 days after exposure to the virus. Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
initial symptoms of monkeypox are similar to flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. However, unlike chickenpox, monkeypox also causes swollen lymph nodes in the affected areas. As the disease progresses, patients may develop a rash that starts on the face before spreading to other parts of the body. The rash usually begins as small red spots that turn into fluid-filled blisters over time .Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
The One notable symptom of monkeypox is its ability to cause lesions in mucous membranes such as inside the mouth and nose or on genitalia. These lesions can be painful and may lead to difficulty eating or speaking for some patients
Severity of Monkeypox:
The severity of monkeypox can vary from person to person depending on their age and overall health condition. In most cases, children tend to have milder symptoms compared to adults.
Although it shares similarities
Emotional impact on patients

The emotional impact of any illness can be just as significant as the physical symptoms, and this is especially true for viral infections like monkeypox and chickenpox. Both illnesses can lead to a range of emotions in patients, from fear and anxiety to frustration and isolation. In this section, we will explore the emotional impact that these two viruses can have on patients. Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
Fear and Anxiety:
One of the most common emotions experienced by patients with monkeypox or chickenpox is fear. This is because both illnesses are highly contagious and can spread rapidly among close contacts. Patients may worry about infecting their loved ones or contracting a more severe form of the virus themselves. The fear may also stem from not knowing how long the illness will last, what complications may arise, or if they will fully recover. Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
Additionally, anxiety levels may rise due to uncertainty surrounding treatment options for these viruses. Since there are currently no specific treatments available for either viral infection, patients may feel helpless or anxious about their recovery process. They may also be concerned about missing work or school while they recover.
Frustration:
Patients with monkeypox or chickenpox often experience frustration due to the uncomfortable nature of their symptoms Monkeypox vs Chickenpox. Both viruses cause itchy rashes that can be difficult to manage and control, leading to feelings of irritation and annoyance. The constant need to scratch can also disrupt sleep patterns, leaving patients feeling exhausted and frustrated.
Isolation:
what is chickenpox ?
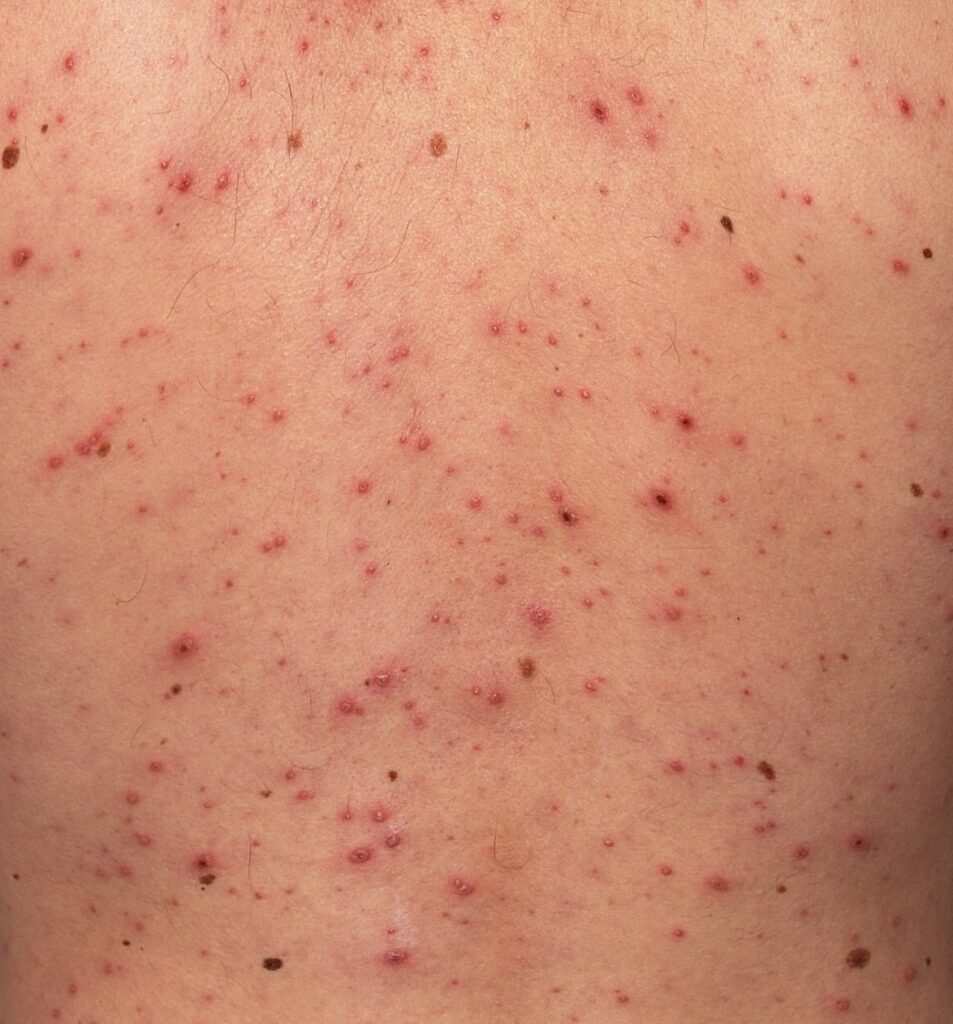
Another emotional impact that patients with monkeypox or chickenpox may fa
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects children. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and can cause a characteristic rash of itchy blisters all over the body. While most cases of chickenpox are mild and resolve on their own within a week or two, it can also lead to serious complications in certain individuals. Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
The virus spreads through direct contact with an infected person’s saliva or respiratory secretions, or through touching objects contaminated with these fluids. It can also be transmitted through airborne particles when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus is most contagious during the first few days before any symptoms appear and remains so until all the blisters have crusted over.
Symptoms of chickenpox typically start with a low-grade fever, headache, and loss of appetite. This is followed by the development of an itchy rash that begins on the face and scalp before spreading to other parts of the body such as the trunk, arms, and legs. The rash starts as red bumps that quickly turn into small fluid-filled blisters within a day or two. These blisters then crust over and eventually fall off, leaving behind scabs that may take several days to heal completely.
While chickenpox is usually more common in children under 12 years old, anyone who has not had chickenpox before or has not been vaccinated against it can get infected at any age. Adults
Definition and History
Monkeypox and chickenpox are both viral infections caused by different types of the poxvirus. They are highly contagious and can cause a variety of symptoms, including rash, fever, and blisters on the skin. However, despite sharing similar names and some common symptoms, these two diseases have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Monkeypox is a rare disease that primarily affects animals in central and western Africa. The first human case was reported in 1970 in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Since then, there have been sporadic outbreaks in African countries such as Cameroon, Central African Republic, Nigeria, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. On the other hand, chickenpox is a much more common disease that has been around for centuries. It was first described by an Italian physician in the 16th century as “water bubbles” or “red spots” on the skin. Before the introduction of a vaccine in 1995, it was estimated that 4 million people got infected with chickenpox every year in the United States alone. History _The history of monkeypox can be traced back to smallpox – another viral infection caused by a closely related virus called Variola virus. Smallpox had been causing deadly epidemics throughout history until its eradication through global vaccination efforts led by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1980.Scientists believe that monkeypox emerged when smallpox vaccines were being developed using live vac Monkeypox vs Chickenpox
Causes and Transmission
causes and Transmission of Monkeypox and Chickenpox
Monkeypox and chickenpox are both caused by viruses, but the strains that cause them are different. While monkeypox is caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), chickenpox is caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV). These viruses belong to different families, with MPXV being a member of the Ortho poxvirus family while VZV belongs to the Herpesviridae family.
Transmission of Monkeypox
The primary mode of transmission for monkeypox is through contact with infected animals, particularly rodents like squirrels, rats, and monkeys. People can also contract the virus from handling infected animal products such as meat or blood. In some cases, human-to-human transmission may occur through close contact with an infected person’s bodily fluids or respiratory secretions.
Transmission of Chickenpox
Chickenpox is highly contagious and can spread easily from person to person through direct contact with respiratory secretions or fluid from blisters. The virus can also be transmitted indirectly through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces. Additionally, people who have not had chicken pox before can get it by coming into close proximity with someone who has shingles caused by reactivation of VZV.
Similarities in Transmission
Both monkeypox and chicken pox share similar routes of transmission; they can both be spread through direct contact or exposure to respiratory secretions and bodily fluids.
Symptoms and Severity
Symptoms and severity are important factors to consider in any illness, as they can greatly impact the overall experience of the affected individual. In the case of monkeypox and chickenpox, both caused by viruses from the same family, their symptoms and severity levels can vary significantly.
Monkeypox is a rare viral disease that was first discovered in 1958 among laboratory monkeys. It is caused by the monkeypox virus (MPXV), which belongs to the Ortho poxvirus genus. The virus is primarily found in animals such as rodents and primates, but it can also infect humans through direct contact with infected animals or animal products.
One of the main symptoms of monkeypox is a rash that appears on various parts of the body, including face, palms, soles, and genitals. The rash starts off as red bumps that eventually turn into blisters filled with fluid. These blisters may crust over and fall off after a few weeks. Other common symptoms include fever, headache, muscle pain, swollen lymph nodes, and fatigue. In severe cases, patients may also experience coughing, difficulty breathing, bleeding from mucous membranes or skin lesions.
The severity of monkeypox varies depending on several factors such as age and underlying health conditions of the patient. Generally speaking, young children tend to have milder symptoms compared to adults who may experience more severe illness with higher mortality rates. People with weakened immune systems due to pre-existing medical conditions or medications are also at a
Emotional impact on patients
The emotional impact of any illness can be just as significant as the physical symptoms it presents. This is especially true when it comes to viral infections, such as monkeypox and chickenpox, which are highly contagious and can cause discomfort and distress for those affected. In this section, we will explore the emotional toll that these two viruses can take on patients.
Firstly, let’s look at how being diagnosed with monkeypox or chickenpox can make a person feel. Both of these illnesses are caused by viral infections and present with similar symptoms such as fever, rash, and body aches. However, in severe cases of monkeypox, patients may also experience severe fatigue and swollen lymph nodes. This sudden onset of symptoms can be overwhelming for some individuals, leading to feelings of fear and anxiety about their health.
Moreover, both monkeypox and chickenpox are highly infectious diseases that require strict isolation to prevent further spread. This means that patients may have to stay home from work or school during their recovery period, causing disruption to their daily routine. For children who contract chickenpox, missing school may mean falling behind on studies or missing out on important social activities with friends.
Another significant aspect of the emotional impact of these illnesses is the discomfort and pain they cause. The rashes associated with monkeypox and chickenpox can be extremely itchy and uncomfortable for patients. This constant irritation can lead to frustration and irritability in both adults and children alike. Furthermore, if
Comparison between Monkeypox and Chickenpox

Introduction:
Monkeypox and chickenpox are two viral infections that cause skin rashes and fever. Both of these diseases have similar symptoms, but they are caused by different viruses. In this section, we will compare the two infections in terms of their causes, symptoms, transmission, treatment, and prevention.
Causes:
Monkeypox is caused by a virus called monkeypox virus (MPXV), a member of the Orthopoxvirus genus. This virus is closely related to the variola virus which causes smallpox. On the other hand, chickenpox is caused by varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which belongs to the herpesvirus family.
Symptoms:
Both monkeypox and chickenpox cause similar symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue, and body aches. However, there are some distinct differences between the rashes they produce. Monkeypox rashes usually start on the face before spreading to other parts of the body while chickenpox rashes typically begin on the trunk before spreading outwards. Chickenpox rashes also tend to be more itchy compared to monkey pox.
Transmission:
Monkeypox and chicken pox are highly contagious diseases that can spread through close contact with an infected person or through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing. However, monkey pox can also be transmitted through contact with bodily fluids or contaminated objects such as bedding or clothing. Chicken pox can only